Pimples are a universal skin concern that many of us face at some point in our lives. Whether you’re battling an occasional breakout or chronic acne, understanding the types of pimples can help you target treatments more effectively. In this article, we’ll delve into the seven most common types, their causes, and treatment options to help you maintain healthier, clearer skin.
What Are Pimples and Why Do They Occur?
Pimples, scientifically referred to as acne vulgaris, are small skin lesions or inflammations resulting from clogged pores. Factors such as excess sebum production, dead skin cells, bacteria, and hormonal changes can all lead to pimple formation. Identifying the specific types of pimples you have is crucial for proper management.
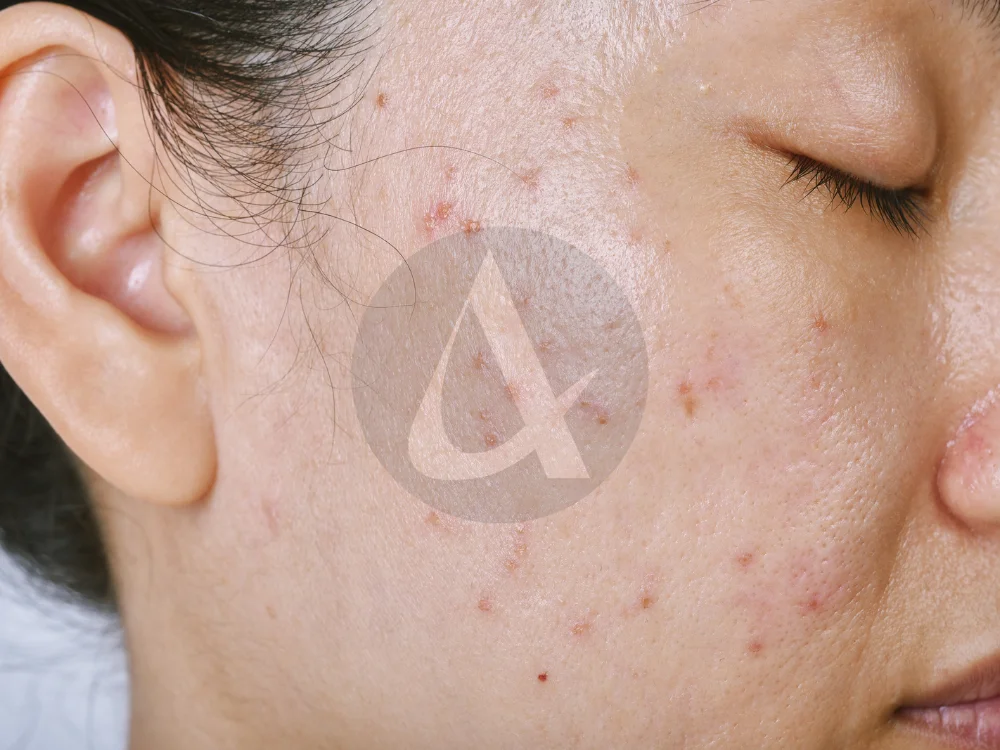
1. Whiteheads (Closed Comedones)
Whiteheads are small, white bumps that form when pores are clogged with oil and dead skin cells. Unlike blackheads, whiteheads remain closed, which gives them their characteristic white appearance.
Causes of Whiteheads
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Poor skincare routine
- Excessive use of oily products
Treatment for Whiteheads
- Use salicylic acid-based cleansers to gently exfoliate.
- Apply benzoyl peroxide to target bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Incorporate non-comedogenic products into your skincare routine.
2. Blackheads (Open Comedones)
Blackheads occur when pores are clogged but remain open, allowing trapped debris to oxidize and turn black.
Causes of Blackheads
- Overproduction of oil
- Improper cleansing
- Environmental pollutants
Treatment for Blackheads
- Regular exfoliation with products containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs).
- Topical retinoids like adapalene to prevent clogging.
- Avoid manual extraction, as it can cause skin damage.
3. Papules
Papules are small, raised, red bumps that occur when pore walls break down due to severe clogging, leading to inflammation. Unlike whiteheads and blackheads, papules do not contain pus.
Causes of Papules
- Bacterial infections in pores
- Excessive oil production
- Hormonal imbalances
Treatment for Papules
- Spot-treat with benzoyl peroxide to minimize bacteria.
- Use soothing anti-inflammatory products like niacinamide.
- Avoid picking or squeezing to prevent scarring.
4. Pustules
Pustules are similar to papules but contain pus, giving them a white or yellow center surrounded by red inflammation.
Causes of Pustules
- Immune response to bacteria
- Overuse of heavy skincare products
- Hormonal fluctuations
Treatment for Pustules
- Apply sulfur-based spot treatments to reduce pus.
- Use topical antibiotics prescribed by a dermatologist.
- Maintain a consistent skincare routine to manage oil production.

5. Nodules
Nodules are large, painful lumps that develop deep within the skin. They are one of the more severe types of pimples, often requiring professional treatment.
Causes of Nodules
- Severe bacterial infection in the pores
- Genetic predisposition to acne
- Hormonal acne flare-ups
Treatment for Nodules
- Seek help from a dermatologist for oral medications like isotretinoin.
- Cortisone injections may be necessary for severe cases.
- Avoid over-the-counter treatments, as they might not penetrate deeply enough.
6. Cysts
Cystic acne is the most severe type of acne, characterized by large, pus-filled lesions that are often painful and prone to scarring.
Causes of Cysts
- Deep-seated bacterial infections
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal changes, especially during puberty
Treatment for Cysts
- Oral medications such as isotretinoin or antibiotics.
- Topical retinoids to prevent clogged pores.
- Surgical drainage for extremely severe cases (performed by a dermatologist).
7. Fungal Acne (Malassezia Folliculitis)
Fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of yeast rather than bacteria, leading to itchy, uniform bumps often mistaken for regular acne.
Causes of Fungal Acne
- Excessive sweating
- Wearing tight clothing for long periods
- Use of heavy, oil-based skincare products
Treatment for Fungal Acne
- Antifungal treatments like ketoconazole cream.
- Wash with dandruff shampoo containing zinc pyrithione.
- Avoid occlusive skincare products that trap moisture.
How to Prevent Pimples
While treatment is essential, prevention is equally important. Here are some practical tips:
- Cleanse Regularly: Use a gentle, pH-balanced cleanser twice daily.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Hands carry bacteria that can aggravate acne.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps maintain skin balance.
- Choose the Right Products: Opt for non-comedogenic and fragrance-free skincare items.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate acne through hormonal changes.
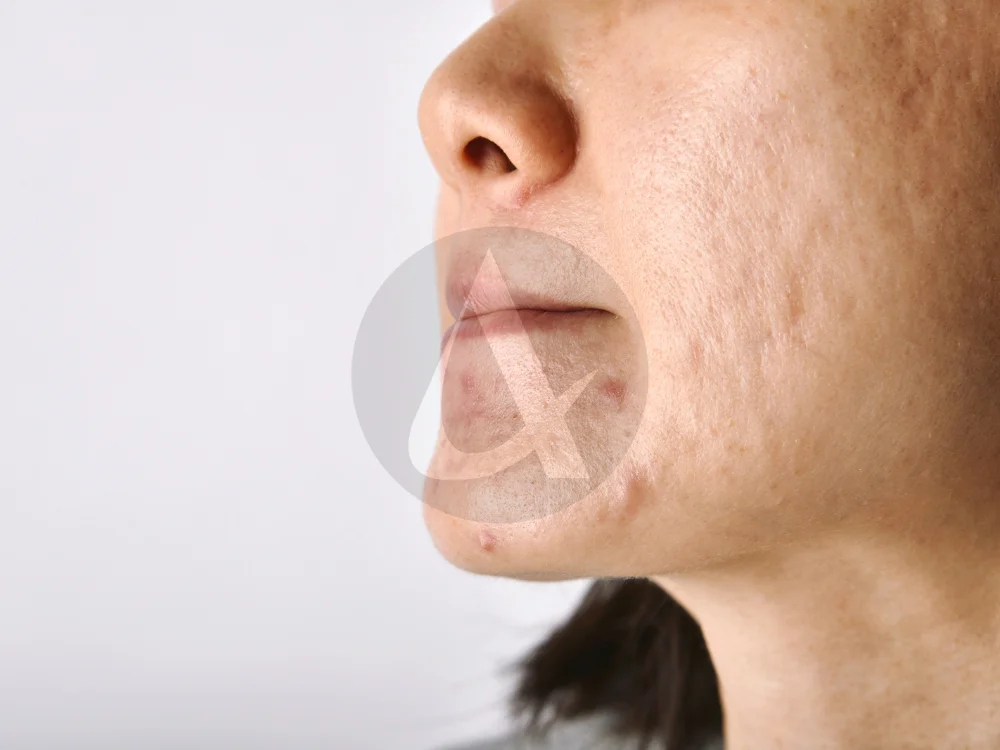
FAQs About Types of Pimples
1. How can I tell what type of pimple I have?
Identifying your pimple type requires observation. Whiteheads and blackheads are non-inflammatory, while papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts show redness and swelling.
2. Can I treat all types of pimples at home?
Mild acne like whiteheads and blackheads can often be managed at home. For severe acne types like nodules or cysts, professional dermatological treatment is recommended.
3. Are natural remedies effective for pimples?
Some natural remedies like tea tree oil or aloe vera can help mild acne, but their efficacy varies. Always patch-test and consult a dermatologist for severe cases.
4. What’s the difference between fungal acne and regular acne?
Fungal acne is caused by yeast and is often itchy, while regular acne is bacterial and may include pus-filled lesions.
5. Does diet affect the formation of pimples?
Yes, diets high in sugar and dairy can trigger acne in some individuals. Opt for a balanced diet rich in vegetables and low in processed foods.
6. Can makeup cause pimples?
Yes, especially if you use heavy or non-comedogenic products. Always remove makeup thoroughly before bed to prevent clogging pores.
Conclusion
By understanding the types of pimples and their specific treatments, you can take informed steps toward achieving clearer, healthier skin. Tailor your skincare routine to suit your needs and consult a professional for persistent or severe cases.
