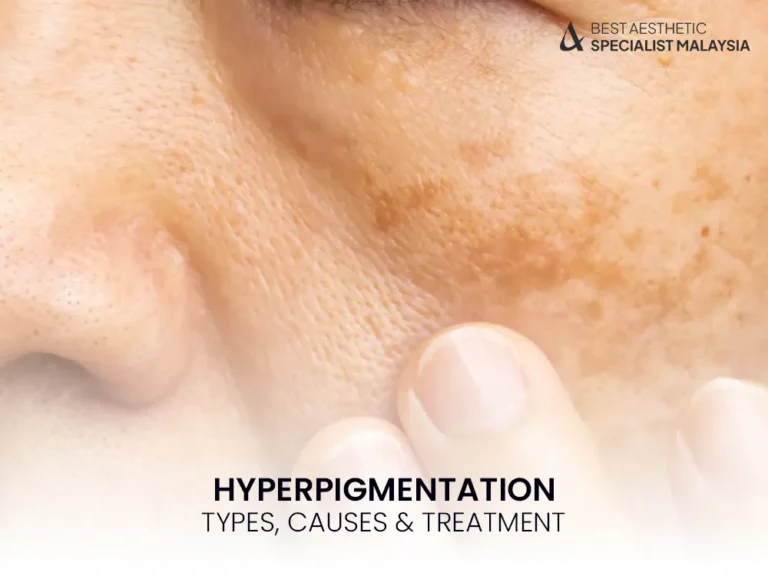
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that leads to darkened patches or spots due to excess melanin production. It can affect anyone but is more prominent in people with medium to darker skin tones.
Whether triggered by sun exposure, acne scars, hormones, or skin injuries, hyperpigmentation is treatable with the right skincare routine or clinical procedure.
In this guide, we explore what hyperpigmentation is, the different types, common causes, and dermatologist-recommended treatments.
What Is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation occurs when your skin produces too much melanin, the pigment responsible for your natural skin color. This leads to dark patches or uneven skin tone, especially on areas exposed to the sun.
It can be localized (as in acne marks or age spots) or more widespread (like melasma).
Common Types of Hyperpigmentation
1. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Caused by acne, eczema, or skin trauma. Appears as flat, dark spots where inflammation occurred.
2. Melasma
Triggered by hormonal changes, especially in pregnancy or birth control use. Common on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip.
3. Sunspots (Lentigines)
Also known as age spots, these are caused by long-term UV exposure and usually appear on the face, neck, or hands.
4. Freckles
Genetically inherited and influenced by sun exposure. Usually harmless but may darken over time.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation?
Sun Exposure – UV rays stimulate melanin production
Inflammation or Injury – Acne, cuts, or burns can trigger melanin overproduction
Hormonal Changes – Estrogen and progesterone affect pigment cells
Medications – Some antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs can darken skin
Genetics – Family history can increase your risk
How to Treat Hyperpigmentation
Effective treatment depends on severity, skin type, and underlying cause. Options include:
1. Topical Creams
Hydroquinone – Skin-lightening agent (prescription only in many countries)
Niacinamide – Reduces inflammation and pigment production
Azelaic Acid – Especially effective for PIH and acne-prone skin
Retinoids (Tretinoin) – Promote skin turnover and fading of marks
Vitamin C – Brightens and protects skin from oxidative stress
Note: Use sunscreen daily to prevent further pigmentation.
2. Chemical Peels
Light to medium-depth peels using glycolic acid, salicylic acid, or TCA exfoliate the top layer of skin, reducing pigmentation.
May require multiple sessions and post-care with sunscreen and moisturizer.
3. Laser Treatments
Laser Toning (Q-switched ND:YAG) – Breaks down melanin without harming surrounding tissue
Fractional Lasers – Stimulate collagen and help resurface pigmented skin
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) – Works on superficial pigment and sunspots
Laser treatments are best performed by experienced, board-certified aesthetic doctors, especially for darker skin tones.
4. Microneedling with PRP
Encourages skin regeneration and can help fade stubborn pigmentation when combined with topical agents or platelet-rich plasma (PRP).
Prevention Tips for Hyperpigmentation
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) daily
Avoid picking or squeezing pimples
Wear protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat when outdoors
Choose gentle skincare to prevent irritation
Consult a professional before trying strong actives like acids or retinoids
When to See a Doctor
See a dermatologist or licensed aesthetic provider if:
The pigmentation spreads, worsens, or darkens quickly
OTC products are ineffective after 2–3 months
You have underlying skin conditions like eczema, acne, or hormonal imbalance
You’re unsure whether the condition is pigmentation or something else (e.g., melanoma)
Final Thoughts
Hyperpigmentation is a treatable skin concern, but results take time and consistency. Whether through targeted skincare, chemical peels, or laser treatments, working with a professional helps ensure you’re using safe and effective methods suited to your skin type.
At Best aesthetic centre, we offer a range of evidence-based pigmentation treatments customized for Asian skin tones, ensuring safe and visible results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can hyperpigmentation go away on its own?
Mild cases may fade over time, but moderate to severe pigmentation often needs professional treatment.
2. Is laser treatment safe for dark skin?
Yes. Q-switched lasers and specific IPL settings can safely treat pigmentation in darker skin, but should be performed by experienced practitioners.
3. How long does it take to see results?
Topical treatments may show improvement in 4–8 weeks, while laser or peels may deliver faster results but require multiple sessions.
4. Can sunscreen treat pigmentation?
Sunscreen doesn’t reverse pigmentation, but it’s critical to prevent further darkening and protect results from treatments.
5. What’s the best treatment for melasma?
Combination therapy: topical lighteners, chemical peels, strict sun protection, and sometimes oral tranexamic acid under medical supervision.
Experts Insights
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition where areas of skin develop spots or patches darker than the surrounding skin tone. These changes are often linked to sun exposure, UV rays, and sun damage, which trigger excess melanin production. Age spots and liver spots are classic examples, while other skin conditions may also cause patches of skin to appear uneven. Dermatologists often recommend topical treatments such as azelaic acid and skin lightening creams, along with professional options like chemical peels or laser treatment, depending on the severity and the patient’s medical condition.
Managing hyperpigmentation requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on both correction and prevention. Patients may benefit from treatments designed to treat hyperpigmentation, including targeted laser treatment and topical treatments, but ongoing care is equally important. Protecting your skin daily with broad-spectrum sunscreen containing zinc oxide or SPF 30 helps reduce further darkening of spots or patches caused by sun exposure. A personalized plan combining clinical therapies, skin lightening products, and lifestyle adjustments ensures more even results, while addressing the underlying skin conditions that contribute to hyperpigmentation.